

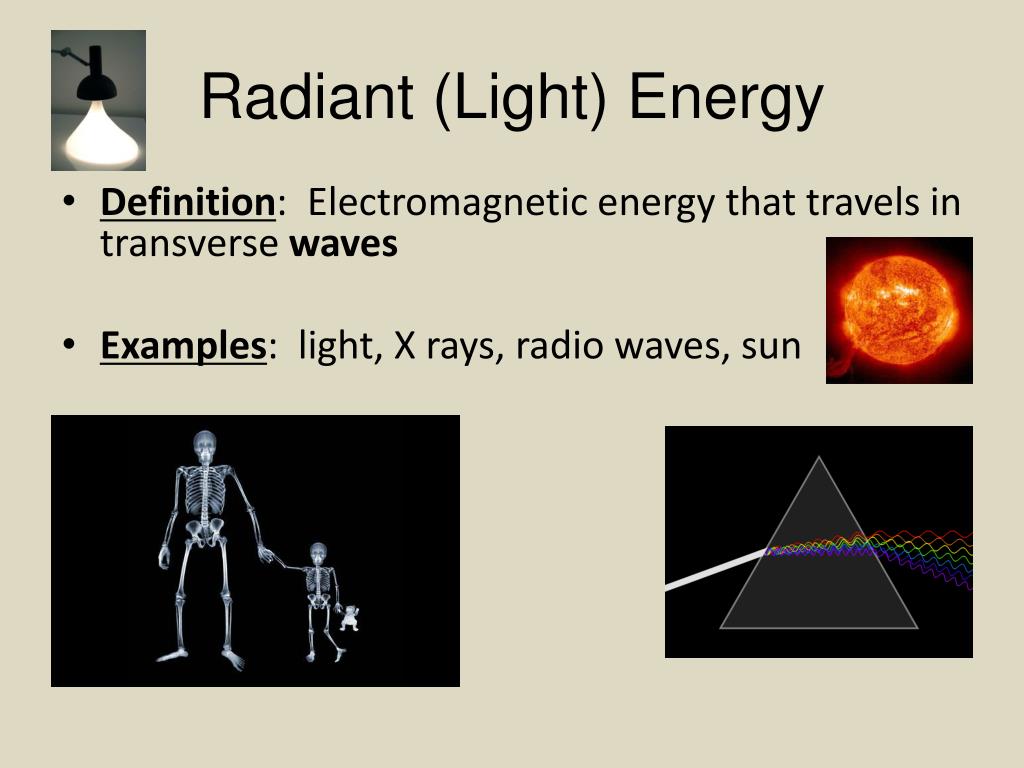
Under intense pressure and high temperatures, these remains became what we know as fossil fuels. This process continued for millions of years. After the autotrophs died, they decomposed and shifted deeper into the Earth, sometimes thousands of meters. Sunlight allowed plant life to thrive and evolve. Scientists estimate that about three billion years ago, the first autotrophs evolved in aquatic settings. Fossil Fuels Photosynthesis is also responsible for all of the fossil fuels on Earth. Detritivores decompose plant and animal matter by consuming it. Carnivores and omnivores eat both producers and herbivores. Herbivores eat plants and other producers. Herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and detritivores rely on solar energy indirectly. Consumers rely on producers for nutrients. Autotrophs are the foundation of the food web. Producers, also called autotrophs, include plants, algae, bacteria, and fungi. They absorb sunlight and convert it into nutrients through a process called photosynthesis. Photosynthesis Almost all life on Earth relies on solar energy for food, either directly or indirectly. This greenhouse effect keeps Earth warm enough to sustain life. In this way, they act like the glass walls of a greenhouse. Greenhouse gases trap the heat that reflects back up into the atmosphere. As they rise through the atmosphere, they are intercepted by greenhouse gases, such as water vapor and carbon dioxide. The radiation warms Earth’s surface, and the surface radiates some of the energy back out in the form of infrared waves. The rest is absorbed into Earth’s atmosphere. Natural Solar Energy Greenhouse Effect The infrared, visible, and UV waves that reach Earth take part in a process of warming the planet and making life possible-the so-called “greenhouse effect.” About 30 percent of the solar energy that reaches Earth is reflected back into space. The color red has the longest wavelengths (closest to infrared), and violet (closest to UV) the shortest. Sandwiched between infrared and UV is the visible spectrum, which contains all the colors we see on Earth. Most heat from the sun arrives as infrared energy. The sun also emits infrared radiation, whose waves are much lower-frequency. Less potent UV rays travel through the atmosphere, and can cause sunburn. The most harmful UV rays are almost completely absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere. The most high-frequency waves emitted by the sun are gamma rays, X-rays, and ultraviolet radiation (UV rays). The vast majority of electromagnetic waves are invisible to us. In contrast, low-frequency waves have much longer wavelengths. Waves with very short wavelengths repeat themselves several times in a given unit of time, so they are high-frequency. The frequency of a wave represents how many times the wave repeats itself in a certain unit of time.
The electromagnetic spectrum exists as waves of different frequencies and wavelengths. The energy, heat, and light from the sun flow away in the form of electromagnetic radiation (EMR). Solar energy warms Earth, causes wind and weather, and sustains plant and animal life. Solar energy is constantly flowing away from the sun and throughout the solar system. Nuclear fusion by the PP chain reaction or CNO cycle releases tremendous amounts of energy in the form of waves and particles. Currently, less than two percent of the sun’s energy is created by the CNO cycle. The CNO cycle also converts hydrogen to helium, but relies on carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen (C, N, and O) to do so. In stars that are about 1.3 times bigger than the sun, the CNO cycle drives the creation of energy.

The temperature for these stars is around 4 million degrees on the Kelvin scale (about 4 million degrees Celsius, 7 million degrees Fahrenheit). The PP chain reaction occurs in other stars that are about the size of our sun, and provides them with continuous energy and heat. In its core, the sun fuses about 620 million metric tons of hydrogen every second. This process, known as a PP (proton-proton) chain reaction, emits an enormous amount of energy. Fusion occurs when protons of hydrogen atoms violently collide in the sun’s core and fuse to create a helium atom. Solar energy is created by nuclear fusion that takes place in the sun. Solar energy is any type of energy generated by the sun.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
